
Introduction to Web Hosting
Web hosting is a fundamental component of the internet’s infrastructure, making it possible for websites to be accessible online. At its core, web hosting refers to a service that enables individuals or organizations to publish their websites on the internet. A web host, also known as a hosting provider, allocates space on a server for a website’s files, making them available for viewing online.
The importance of web hosting lies in its role as the backbone of website accessibility. Without a proper hosting service, a website cannot be accessed by users, regardless of how well-designed or informative it may be. Essentially, web hosting ensures that your website is stored on a server and connected to the internet, allowing anyone with an internet connection to visit your site.
Web hosting operates through various key components. The primary element is the server, which acts as a powerful computer that stores your website’s files and data. These servers are maintained and managed by hosting providers to ensure constant uptime and reliability. Another critical component is the domain name, which serves as the address of your website. When users type your domain name into a browser, it directs them to your web host’s server, where the website’s files are stored.
Storage space is another significant aspect of web hosting. It pertains to the amount of data your website can store on the host’s server, including HTML files, images, videos, and other multimedia content. Depending on the hosting plan you choose, the amount of storage can vary, accommodating different types of websites ranging from small blogs to large e-commerce sites.
In summary, web hosting is essential for the operational visibility of any website. By understanding its core components and functionality, users can make informed decisions about their hosting needs, ensuring their websites remain accessible and efficient.
Types of Web Hosting Services
When embarking on a journey to create a website, understanding the various types of web hosting services is crucial. The choice of hosting service can influence website performance, security, and scalability. Here, we delineate the five primary types: shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated hosting, cloud hosting, and managed hosting.
Shared Hosting is the most popular and economical option, where numerous websites share a single physical server. This shared environment means resources like CPU, RAM, and disk space are distributed among all websites hosted on that server. The primary advantage is its affordability and ease of setup, making it an excellent choice for small businesses and personal websites. However, the downside is potential performance slowdowns and limited control over server settings due to shared resources.
VPS Hosting (Virtual Private Server) offers a middle ground between shared and dedicated hosting. It involves partitioning a single physical server into multiple virtual servers, each acting independently. VPS hosting provides greater control, scalability, and improved performance compared to shared hosting. It is particularly suitable for growing websites that require more resources without the higher cost of a dedicated server. Nonetheless, it demands more technical knowledge for management and can still encounter resource limitations.
Dedicated Hosting is an advanced option where an entire physical server is dedicated to a single website. This exclusivity affords maximum performance, control, and security. Dedicated hosting is ideal for large enterprises with high traffic and resource-intensive applications. However, its benefits come at a higher cost and require substantial technical expertise to manage effectively.
Cloud Hosting represents a modern and flexible hosting solution utilizing a network of interconnected servers. Websites hosted on the cloud can dynamically scale resources based on real-time demand, ensuring high availability and reliability. Cloud hosting is particularly beneficial for websites with fluctuating traffic patterns. The primary drawback could be its complex pricing structure, which can fluctuate based on resource usage.
Managed Hosting involves a dedicated team of professionals managing the server on behalf of the user. It includes services like server maintenance, updates, and security management. Managed hosting is ideal for businesses that prefer to focus on their core operations without worrying about technical aspects. However, it tends to be more expensive due to the added layer of professional support.
Understanding these web hosting options and their characteristics enables better decisions aligning with specific needs and growth plans. Each type offers distinct advantages and potential drawbacks, ensuring there is a suitable solution for every web hosting requirement.
Choosing the Right Hosting Provider
When it comes to selecting the ideal hosting provider, several critical factors must be scrutinized to ensure you make an informed decision. The first aspect to consider is reliability. A reliable hosting provider guarantees that your website will operate smoothly with minimal downtime. Uptime, an essential measure of a hosting service’s reliability, is typically expressed as a percentage. Providers that offer 99.9% uptime or higher are generally more dependable, ensuring your website remains accessible to visitors almost all the time.
Customer support is another pivotal element. Opt for a hosting provider that offers robust customer service, available 24/7. This feature is particularly crucial if you encounter any technical difficulties or need assistance with your hosting setup. Look for providers that offer multiple support channels, including live chat, email, and phone support.
Scalability is essential for businesses expecting growth. A hosting provider that offers scalable solutions enables you to upgrade your hosting plan effortlessly as your website expands and traffic increases. This flexibility ensures that your hosting service can grow with your business needs without causing any disruptions.
Cost is always a consideration, but it shouldn’t be the only factor. Lower-priced hosting plans might be appealing, but they often come with limitations, such as fewer features or lower performance. It’s important to balance cost with the features and performance your website requires. Look for hosts that offer a variety of plans, allowing you to choose one that fits your budget while still meeting your needs.
The features provided by the hosting service are equally important. Features such as bandwidth, storage, control panel ease of use, and availability of one-click installs for popular software can significantly impact your site’s functionality and your experience managing it. Evaluate the features offered by different providers to ensure they align with your website requirements.
Reading reviews and comparing different providers can also be very informative. Look at independent review sites and user feedback to get an idea of the real-world performance and customer satisfaction levels of various hosting services. These reviews can provide insights into the reliability, support, and overall quality of the hosting providers under consideration.
By carefully evaluating these factors—reliability, uptime, customer support, scalability, cost, and features—you’ll be better equipped to choose a hosting provider that meets your needs and supports your website’s success.
Setting Up Your Hosting Account
Setting up a hosting account is the first crucial step to getting your website online. Choosing the right hosting provider and plan can significantly impact your website’s performance. First, you’ll need to register an account with a hosting provider of your choice. Popular providers include Bluehost, Hostgator, and SiteGround. You will be asked to provide basic information such as your name, email address, and payment details. Ensure you select a secure password to protect your account.
Next, you will be required to select a hosting plan. Most providers offer several plans, ranging from basic to advanced options. If you’re starting with a simple website or blog, a basic plan will usually suffice. These plans typically include shared hosting, where your website shares server resources with other sites. For more intensive needs, consider VPS or dedicated hosting, which offers more resources and better performance.
After selecting a plan, the next step is to purchase a domain name, if you don’t already have one. Your domain name is your website’s address on the internet, such as www.yourwebsite.com. Many hosting providers offer a free domain for the first year with their hosting plans. Choose a domain name that is easy to remember and relevant to your content.
Finally, you will configure your initial account settings. This usually involves selecting your preferred server location, choosing the software or content management system (CMS) you plan to use (such as WordPress), and setting up your email accounts. Most hosting providers offer a user-friendly control panel to facilitate these configurations. Some control panels, like cPanel, provide extensive documentation to help you get started easily. Upon completing these steps, your hosting account should be ready, and you can proceed with building and customizing your website.
Domain Name Management
Effective domain name management plays a crucial role in establishing and maintaining your online presence. When you acquire a domain, understanding how to manage it in conjunction with your hosting account is essential. The Domain Name System (DNS) serves as a critical component in this process. Essentially, DNS translates human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network.
The first step in domain name management is pointing your domain to your hosting account. This usually involves updating the domain’s DNS settings with the IP address or nameservers provided by your hosting provider. Most hosting providers make this process straightforward through user-friendly control panels. For instance, if you’re using a popular hosting service like Bluehost or GoDaddy, their interfaces typically offer step-by-step instructions or even automated tools to assist in this task.
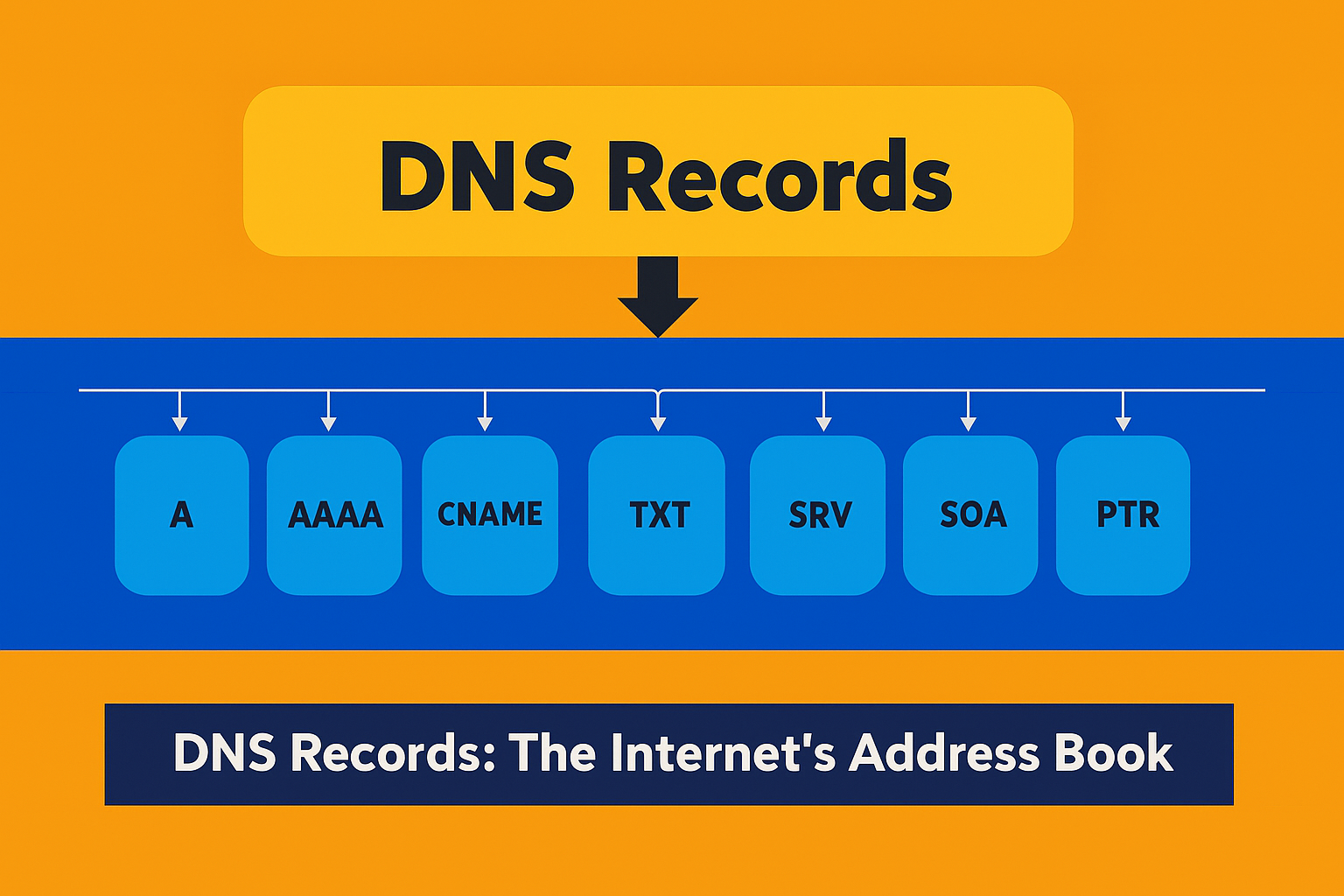
Once your domain is pointed to your hosting account, managing DNS records becomes vital. Common types of DNS records include A records, which map your domain to a specific IP address, CNAME records for aliasing one domain name to another, and MX records, which are used for email routing. Adjusting these records as per your needs ensures that your domain functions correctly and efficiently directs traffic to your website.
Most hosting providers offer comprehensive tools for domain management. Control panels such as cPanel, Plesk, and proprietary dashboards give users the ability to edit DNS records, set up subdomains, and manage email settings. With these tools, you can also perform advanced tasks like setting up domain-specific email addresses and configuring your website’s security settings.
Understanding the basics of domain name management and utilizing the tools provided by your hosting provider will help ensure that your website remains accessible and professional, enhancing your overall online strategy. Effective management not only simplifies the domain setup process but also fortifies your site’s dependability and functionality in the long run.
Setting Up a Website on Your Host
Once you have secured a hosting service, the next step is to set up your website on the host. This process involves installing a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, uploading website files via File Transfer Protocol (FTP), or utilizing site builders that are often provided by hosting services. Here, we will go through each of these methods to help you get started.
To begin with, installing a CMS such as WordPress is a popular choice for many due to its user-friendly interface and extensive plugin ecosystem. Most hosting providers offer a one-click installation feature for WordPress. Navigate to your hosting control panel, locate the one-click installer, select WordPress, and follow the on-screen instructions. This will set up the necessary databases and install the CMS.
If you prefer uploading website files directly, using FTP is an effective method. To do this, you need an FTP client such as FileZilla. First, obtain your FTP credentials from your hosting service. Open your FTP client and enter the server address, username, and password. Once connected, navigate to the public_html directory (or similar) and upload your website files. This method grants you greater control over file management and structure.
Alternatively, many hosting providers offer integrated site builders that allow you to design your site without any coding knowledge. These builders come with drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built templates, making it easy to customize your site quickly. Simply log in to your hosting control panel, choose the site builder option, select a template, and start customizing.
Regardless of the method you choose, implementing basic security measures is critical. Ensure you activate SSL certificates to encrypt data transmission. Additionally, setting up firewalls and regular backups will protect your site from potential threats. In your CMS, consider enabling features like two-factor authentication and installing security plugins.
Finally, performing initial configuration settings will smooth out the process. For WordPress users, setting permalinks, creating essential pages (like Contact and About), and configuring site settings through the dashboard are vital steps. If you are using an FTP client or site builder, similarly ensure your site’s basic settings align with your needs.
With these steps, you are now well-equipped to set up your website on your hosting service efficiently, allowing you to focus on creating content and growing your online presence.
Basic Hosting Maintenance
Effective hosting maintenance is essential in ensuring your website operates efficiently and remains secure. Regular maintenance tasks help in optimizing performance, securing data, and providing a seamless experience for users. The process might seem overwhelming initially, but breaking it down into manageable tasks can simplify it.
Firstly, consistently updating your software is crucial. This includes your content management system (CMS), plugins, themes, and server software. Software updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities and performance enhancements. Neglecting updates can expose your website to security threats and hamper its performance. Tools such as WP-CLI for WordPress allow for automating updates, reducing manual intervention while ensuring your website remains up-to-date.
Secondly, regular backups are a lifeline in maintaining your hosting environment. Backups ensure that you can restore your website to a previous state in case of any unexpected errors or security breaches. Automated backup solutions like Jetpack Backup or UpdraftPlus can schedule daily, weekly, or monthly backups, providing peace of mind that your data is secure.
Thirdly, monitoring website performance is key to identifying and mitigating issues that could affect user experience. Tools like Google Analytics and GTmetrix help in tracking load times, visitor behavior, and other metrics. These insights guide you in making necessary adjustments to your website’s structure and content to improve performance.
Additionally, performing regular security checks is vital. Employ security plugins and tools such as Sucuri, Wordfence, or SiteLock, which can scan for malware, monitor for hacking attempts, and provide comprehensive reports on your website’s security status. Regular security audits help in detecting vulnerabilities early and reinforcing your website’s defenses against potential threats.
Overall, basic hosting maintenance encompasses software updates, regular backups, performance monitoring, and security checks. Utilizing automation tools and services can streamline these tasks, making maintenance more manageable and ensuring your website remains robust and reliable.
Troubleshooting Common Hosting Issues
As reliance on digital platforms intensifies, encountering hosting issues can significantly impact a website’s performance and user experience. Understanding how to troubleshoot these common problems is crucial for maintaining a smooth online presence.
Downtime
Website downtime refers to periods when the site is inaccessible. This issue can result from server failures, scheduled maintenance, or unexpected traffic surges. When experiencing downtime, first confirm the issue using online tools such as “Is it down right now?” or “Down For Everyone Or Just Me.” If confirmed, check your hosting provider’s website or support channels for any mentions of ongoing maintenance or known outages. Consider upgrading to a more robust hosting plan if traffic surges frequently cause downtime.
Slow Website Performance
Slow website performance can negatively affect user experience and SEO rankings. Begin by analyzing your site’s speed with tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix. Optimize images, leverage browser caching, and minimize HTTP requests to improve performance. Additionally, evaluate your hosting plan—shared hosting might not provide sufficient resources for high-traffic websites. In such cases, upgrading to VPS (Virtual Private Server) or dedicated hosting can offer better speed and performance.
Security Breaches
Ensuring website security is paramount to safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining user trust. Common security issues include malware infections and unauthorized access. Employ a security plugin and regularly update all software, including the content management system (CMS), themes, and plugins. Set strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for critical accounts. Monitor your site with tools like Sucuri SiteCheck to detect vulnerabilities or malware, and contact your hosting provider’s support team for assistance in resolving security breaches.
Email Deliverability Issues
Email deliverability issues, such as emails being marked as spam or not being delivered, can stem from various factors. Ensure that your domain’s DNS settings include proper SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records, which authenticate emails sent from your domain. Regularly check if your IP is blacklisted using tools like MXToolBox and follow best practices to avoid spammy content. If issues persist, contact your hosting provider to investigate further or to consider dedicated email hosting services.
While these troubleshooting measures can resolve many common hosting issues, don’t hesitate to contact support if problems persist. Hosting providers typically offer technical assistance to help troubleshoot and rectify these issues swiftly.



0 Comments